Customizing Transitions
You can customize the transition behavior of individual actions by assigning a transitionDelegate to the SwipeAction type.
The provided ScaleTransition type monitors the action button’s visibility as it crosses the threshold, and animates between initialScale and identity. This provides a pop-like
effect as the action buttons are exposed more than 50% of their target width.

let action = SwipeAction(style: .default, title: "More") { action, indexPath in return }
action.transitionDelegate = ScaleTransition.default
The ScaleTransition type provides a static default configuration, but it can also be initiantiated with custom parameters to suit your needs.
You can also easily provide your own completely custom transition behavior by adopting the SwipeActionTransitioning protocol. The supplied SwipeActionTransitioningContext to the delegate methods reflect the current swipe state as the gesture is performed.
Customizing Expansion
Expansion behavior is defined by the properties available in the SwipeExpansionStyle type:
target: The relative target expansion threshold. Expansion will occur at the specified value.additionalTriggers: Additional triggers to useful for determining if expansion should occur.elasticOverscroll: Specifies if buttons should expand to fully fill overscroll, or expand at a percentage relative to the overscroll.completionAnimation: Specifies the expansion animation completion style.minimumTargetOverscroll: Specifies the minimum amount of overscroll required if the configured target is less than the fully exposed action view.targetOverscrollElasticity: The amount of elasticity applied when dragging past the expansion target.
Target
The target describes a location to which the view will scroll when expansion is triggered. A trigger is simply a threshold causing expansion to occur.
The SwipeExpansionStyle.Target enumeration defines the following target options:
.percentage(CGFloat): Percentage of superview’s width (0.0 to 1.0)..edgeInset(CGFloat): Inset from superview’s opposite edge (in points).
By default, the configured target will also act as a trigger. For instance, if a target is configured with .percentage(0.5), expansion will trigger when the view is scrolled more than 50% of its superview.
Additional Triggers
It may be desirable to add additional triggers to complement the default target trigger. For instance, destructive expansion adds a touch threshold, triggering expansion when a touch occurs towards the opposite edge of the view. The SwipeExpansionStyle.Trigger enumeration defines the following options:
.touchThreshold(CGFloat): The trigger a specified by a touch occuring past the supplied percentage in the superview (0.0 to 1.0). The action view must also be fully exposed for this trigger to activate..overscroll(CGFloat): The trigger is specified by the distance past the fully exposed action view (in points).
Elastic Overscroll
When elasticOverscroll is enabled, the action buttons will only fill 25% percent of the additional space provided to the actions view.
Completion Animations
The completion animation occurs on touch up if expansion is actively triggered. The SwipeExpansionStyle.CompletionAnimation enumeration defines the following expansion animation completion style options:
.fill(FillOptions): The default expansion button will completely expand to fill the previous place of the cell..bounce: The expansion will bounce back from the trigger point and hide the action view, resetting the cell.
For fill expansions, you can use the FillOptions type to configure the behavior of the fill completion animation along with the timing of the invocation of the action handler. These options are defined by the ExpansionFulfillmentStyle and HandlerInvocationTiming.
The ExpansionFulfillmentStyle allows you to configure how to resolve the actively filled state . The built-in .destructive, and .destructiveAfterFill expansion styles configure the ExpansionFulfillmentStyle to automatically perform the .delete when the action handler is invoked. This is done by created a FillOptions instance using the static automatic(_ style:timing:) method. When you need to determine this behavior at runtime or coordinate deletion with other animations, you can create a FillOptions instance using the static manual(timing:) function and call action.fulfull(style:) asynchronously after your action handler is invoked.
You can use the HandlerInvocationTiming to configure if the action handler should be invoked .with the fill animation, or .after the fill animation completes. Using the .with option behaves like the stock Mail.app, while the .after option behaves more like the 3rd party Mailbox and Tweetbot apps.
Built-in Styles
The framework provides four built-in SwipeExpansionStyle instances which configure the above components accordingly:
.selection
target: .percentage(0.5)
elasticOverscroll: true
addditionalTriggers: []
completionAnimation: .bounce
.destructive
target: .edgeInset(30)
elasticOverscroll: false
addditionalTriggers: [.touchThreshold(0.8)]
completionAnimation: .fill(.automatic(.delete, timing: .with))
.destructiveAfterFill
target: .edgeInset(30)
elasticOverscroll: false
addditionalTriggers: [.touchThreshold(0.8)]
completionAnimation: .fill(.automatic(.delete, timing: .after))
.fill
target: .edgeInset(30)
elasticOverscroll: false
addditionalTriggers: [.overscroll(30)]
completionAnimation: .fill(.manual(timing: .after))
Button Behavior
It is also possible to customize the button expansion behavior by assigning a expansionDelegate to the SwipeOptions type. The delegate is invoked during the (un)expansion process and allows you to customize the display of the action being expanded, as well as the other actions in the view.
The provided ScaleAndAlphaExpansion type is useful for actions with clear backgrounds. When expansion occurs, the ScaleAndAlphaExpansion type automatically scales and fades the remaining actions in and out of the view. By default, if the expanded action has a clear background, the default ScaleAndAlphaExpansion will be automatically applied by the system.

var options = SwipeOptions()
options.expansionDelegate = ScaleAndAlphaExpansion.default
The ScaleAndAlphaExpansion type provides a static default configuration, but it can also be instantiated with custom parameters to suit your needs.
You can also provide your own completely custom expansion behavior by adopting the SwipeExpanding protocol. The protocol allows you to customize the animation timing parameters prior to initiating the (un)expansion animation, as well as customizing the action during (un)expansion.
Vertically Centered Swipe Actions for Tall Cells
If your cells are tall, then it can be useful to have the swipe actions centered relative to the visible portion of the cell.
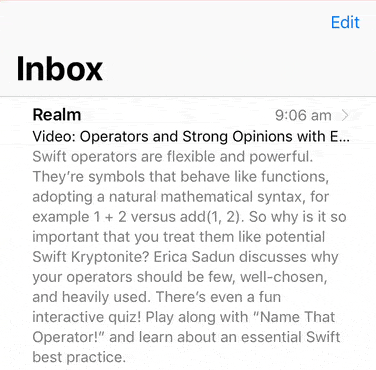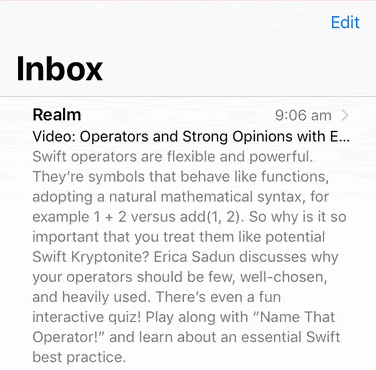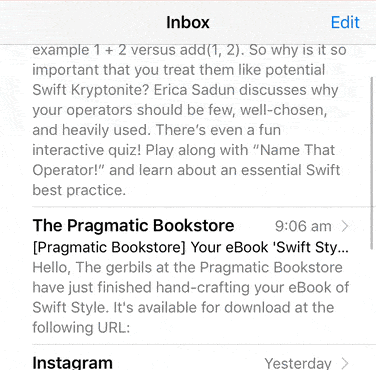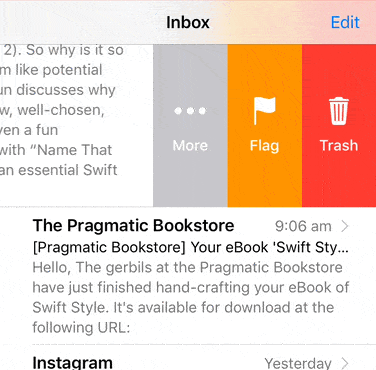
This is enabled once the func visibleRect(for tableView: UITableView) -> CGRect? or func visibleRect(for collectionView: UICollectionView) -> CGRect? in your SwipeTableViewCell‘s or SwipeCollectionViewCell’s delegate returns a non-nil CGRect. This function should return a rectangle of the visible portion of your scroll view (UITableView or UICollectionView) that is in the scroll view’s own coordinate system. The visible portion of the scroll view refers to the part that is not obscurred by other views (e.g. a navigation bar or a toolbar).
If you are targeting iOS 11+ then this is simple thanks to the safe area API and your delegate function could simply be:
func visibleRect(for tableView: UITableView) -> CGRect? {
return tableView.safeAreaLayoutGuide.layoutFrame
}
On earlier iOS versions you will need to calculate this rectangle yourself. In the case where a scroll view controller is embedded in a navigation controller the delegate function could be:
func visibleRect(for tableView: UITableView) -> CGRect? {
let topInset = navigationController?.navigationBar.frame.height ?? 0
let bottomInset = navigationController?.toolbar?.frame.height ?? 0
let bounds = tableView.bounds
return CGRect(x: bounds.origin.x, y: bounds.origin.y + topInset, width: bounds.width, height: bounds.height - bottomInset)
}
Refer to the included Mail app sample to see a working example.
 View on GitHub
View on GitHub Advanced Reference
Advanced Reference